Skin Cancer Prevention: Why Sun Protection Matters
Skin cancer is one of the most common types of cancer in the United States, affecting millions of people each year. It can develop in various forms, from melanoma (the deadliest type) to non-melanoma skin cancers such as basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. However, despite its prevalence, skin cancer is largely preventable, and the most effective way to reduce the risk is through sun protection. In this article, we will discuss why sun protection matters, the types of skin cancer, the risks of sun exposure, and practical tips for preventing skin cancer.
Understanding Skin Cancer
Skin cancer occurs when abnormal skin cells grow uncontrollably. There are three primary types of skin cancer:
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC): BCC is the most common form of skin cancer, making up about 80% of all skin cancer cases. It typically occurs in areas that are frequently exposed to the sun, such as the face, ears, neck, scalp, chest, and back. BCC usually appears as a small, shiny bump or a red patch and grows slowly. While it is rarely fatal, untreated BCC can cause significant tissue damage and disfigurement.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC): SCC is the second most common type of skin cancer. It often appears as a firm, red nodule or a scaly, crusted patch of skin. SCC usually develops on sun-exposed areas of the body, including the face, neck, hands, and arms. Although SCC can spread to other parts of the body, it is highly treatable when caught early.
Melanoma: Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer and can spread rapidly to other parts of the body. It typically begins as a new mole or changes in an existing mole. Melanomas are often dark in color and have irregular borders. Early detection is crucial for improving survival rates, as melanoma can be fatal if left untreated.
The Role of Sun Exposure in Skin Cancer
The primary cause of skin cancer is ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. UV radiation is divided into two main types: UVA and UVB.
UVA Rays: UVA rays penetrate deeply into the skin and are primarily responsible for aging effects, such as wrinkles and age spots. However, they also contribute to skin cancer risk by damaging the DNA in skin cells. UVA rays are present year-round and can penetrate through clouds and windows, making them a year-round threat.
UVB Rays: UVB rays are more intense than UVA rays and are the primary cause of sunburn. These rays damage the outer layers of the skin and play a key role in the development of skin cancer. UVB exposure is stronger during the summer months, at higher altitudes, and closer to the equator.
Both UVA and UVB rays can damage the DNA in skin cells, leading to mutations that can cause cancer. The more sun exposure you have over your lifetime, the higher your risk of developing skin cancer.
Risk Factors for Skin Cancer
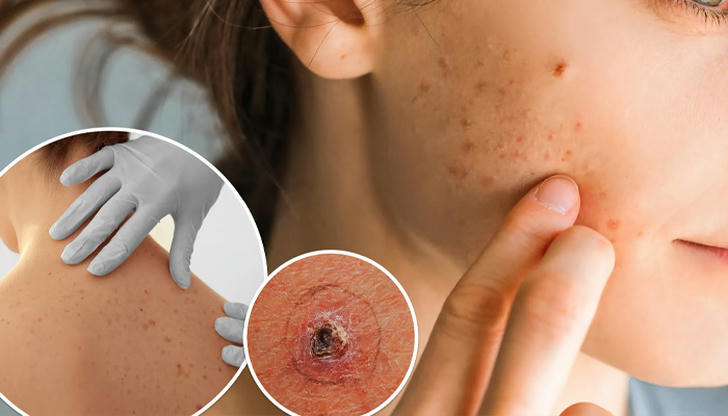
While sun exposure is the most significant risk factor for skin cancer, several other factors can increase your likelihood of developing this condition:
• Fair Skin: People with fair skin, light eyes, and red or blonde hair are more likely to burn than those with darker skin. This is because their skin has less melanin, which provides some protection against UV radiation.
• Family History: If you have a family history of skin cancer, you are at a higher risk of developing it yourself.
• Previous Skin Cancer: If you’ve had skin cancer before, you’re at an increased risk of developing it again.
• Age: The risk of skin cancer increases with age, as accumulated sun damage over the years raises the likelihood of mutations in skin cells.
• Immunocompromised State: People with weakened immune systems, such as those who have undergone organ transplants or who are undergoing chemotherapy, are at greater risk of skin cancer.
• Excessive Sun Exposure: Spending a lot of time in the sun, especially during peak hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.), increases your risk of skin damage and skin cancer.
Why Sun Protection Matters
Sun protection is crucial for reducing the risk of skin cancer, and it is never too late to start protecting your skin. Here are a few reasons why sun protection should be a priority:
Preventing Skin Damage: Sun exposure is the leading cause of skin damage, which includes sunburn, premature aging, and the development of skin cancer. UV radiation can cause direct DNA damage in skin cells, leading to mutations that trigger cancer. By protecting your skin from the sun, you minimize the risk of this damage.
Protecting Against Premature Aging: Sun exposure accelerates skin aging by breaking down collagen and elastin fibers, leading to wrinkles, age spots, and sagging skin. The earlier you start protecting your skin from UV rays, the better your skin will look as you age.
Reducing the Risk of Skin Cancer: Skin cancer is largely preventable, and effective sun protection can significantly lower the risk. Studies show that regular sun protection, such as wearing sunscreen, seeking shade, and wearing protective clothing, can prevent up to 80% of skin cancer cases.
Better Quality of Life: Sun protection allows you to enjoy outdoor activities safely without worrying about the long-term consequences of excessive sun exposure. It helps you maintain healthy, youthful skin and lowers your chances of developing serious health conditions.
Effective Ways to Protect Your Skin from the Sun
There are several practical steps you can take to protect your skin from harmful UV radiation and reduce your risk of skin cancer:
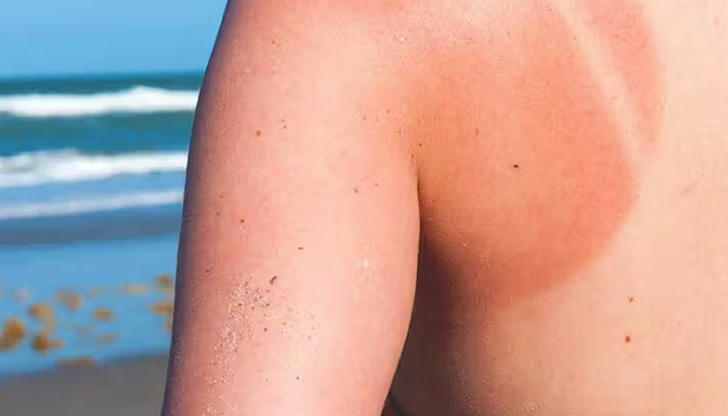

1. Wear Sunscreen Regularly
Sunscreen is one of the most effective ways to protect your skin from UV damage. When choosing a sunscreen, consider the following:
• SPF: Choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30. SPF 30 blocks about 97% of UVB rays, while SPF 50 blocks about 98%.
• Broad-Spectrum Protection: Look for sunscreens labeled "broad-spectrum," as they protect against both UVA and UVB rays.
• Water-Resistant: If you're swimming or sweating, use water-resistant sunscreen to maintain protection.
• Reapply Frequently: Reapply sunscreen every two hours, or more often if you're sweating or swimming. Even if it's cloudy, UV rays can still penetrate the skin.
2. Seek Shade
The sun’s rays are the strongest between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. During these hours, try to stay in the shade as much as possible. If you're going to be outside, seek shade under an umbrella, tree, or other structures.
3. Wear Protective Clothing
Clothing can provide a physical barrier between your skin and the sun. Choose:
• Hats: A wide-brimmed hat that shades your face, neck, and ears is ideal.
• Long-Sleeve Shirts and Pants: Lightweight, long-sleeve shirts and pants made from tightly woven fabrics provide better protection than tank tops and shorts.
• UV-Blocking Clothing: Some clothing brands offer fabrics with built-in UV protection. These clothes are labeled with a UPF rating (Ultraviolet Protection Factor), which indicates how well the fabric blocks UV radiation.
4. Wear Sunglasses
UV rays can damage your eyes and increase the risk of cataracts and other eye conditions. Protect your eyes by wearing sunglasses that block 100% of UVA and UVB rays.
5. Avoid Tanning Beds
Tanning beds emit harmful UV radiation that can increase the risk of skin cancer. It is best to avoid using tanning beds and opt for sunless tanning products instead, which provide a tan without the harmful effects of UV exposure.
The Importance of Regular Skin Checks
In addition to protecting your skin from the sun, regular skin checks are essential for early detection of skin cancer. Early detection increases the chances of successful treatment and recovery. Here’s how to perform a self-skin exam:
• Examine Your Skin: Look for new moles or any changes in existing moles. Pay attention to asymmetry, irregular borders, multiple colors, large size, or any changes in texture.
• Check Hard-to-Reach Areas: Don't forget to check areas like your scalp, the soles of your feet, and the back of your neck.
• Visit a Dermatologist: If you notice any suspicious spots or changes, consult a dermatologist for a professional evaluation.
Conclusion
Skin cancer is preventable, and sun protection plays a critical role in reducing the risk of developing this common and potentially deadly disease. By taking simple precautions like wearing sunscreen, seeking shade, and wearing protective clothing, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of sun damage and skin cancer. Early detection through regular skin checks and visiting a dermatologist can also help ensure that any issues are caught early, making treatment more effective. Remember, it’s never too late to start taking care of your skin – protecting your skin today will benefit you in the long run. Stay safe, stay protected, and enjoy the sun responsibly.
